生成式深度学习

关于
作者
David Foster
译者
Google翻译
译文摘抄
Chapter 2. Deep Learning
第 2 章深度学习
Let’s start with a basic definition of deep learning:
让我们从深度学习的基本定义开始:
Deep learning is a class of machine learning algorithm that uses multiple stacked layers of processing units to learn high-level representations from unstructured data.
深度学习是一类机器学习算法,它使用多个堆叠的处理单元层从非结构化数据中学习高级表示。
To understand deep learning fully, and particularly why it is so useful within generative modeling, we need to delve into this definition a bit further. First, what do we mean by “unstructured data” and its counterpart, “structured data”?
为了充分理解深度学习,特别是为什么它在生成建模中如此有用,我们需要进一步深入研究这个定义。首先,“非结构化数据”及其对应的“结构化数据”是什么意思?
Structured and Unstructured Data
结构化和非结构化数据
Many types of machine learning algorithm require structured, tabular data as input, arranged into columns of features that describe each observation. For example, a person’s age, income, and number of website visits in the last month are all features that could help to predict if the person will subscribe to a particular online service in the coming month. We could use a structured table of these features to train a logistic regression, random forest, or XGBoost model to predict the binary response variable—did the person subscribe (1) or not (0)? Here, each individual feature contains a nugget of information about the observation, and the model would learn how these features interact to influence the response.
许多类型的机器学习算法需要结构化的表格数据作为输入,并将其排列成描述每个观察结果的特征列。例如,一个人的年龄、收入和上个月的网站访问次数都是有助于预测该人在下个月是否会订阅特定在线服务的特征。我们可以使用这些特征的结构化表来训练逻辑回归、随机森林或 XGBoost 模型来预测二元响应变量 - 该人订阅了 (1) 还是不订阅 (0)?在这里,每个单独的特征都包含有关观察的大量信息,并且模型将了解这些特征如何相互作用以影响响应。
Unstructured data refers to any data that is not naturally arranged into columns of features, such as images, audio, and text. There is of course spatial structure to an image, temporal structure to a recording, and both spatial and temporal structure to video data, but since the data does not arrive in columns of features, it is considered unstructured, as shown in Figure 2-1.
非结构化数据是指任何未自然排列成特征列的数据,例如图像、音频和文本。当然,图像有空间结构,记录有时间结构,视频数据也有空间和时间结构,但由于数据不是以特征列形式到达的,因此被认为是非结构化的,如图 2-1 所示。
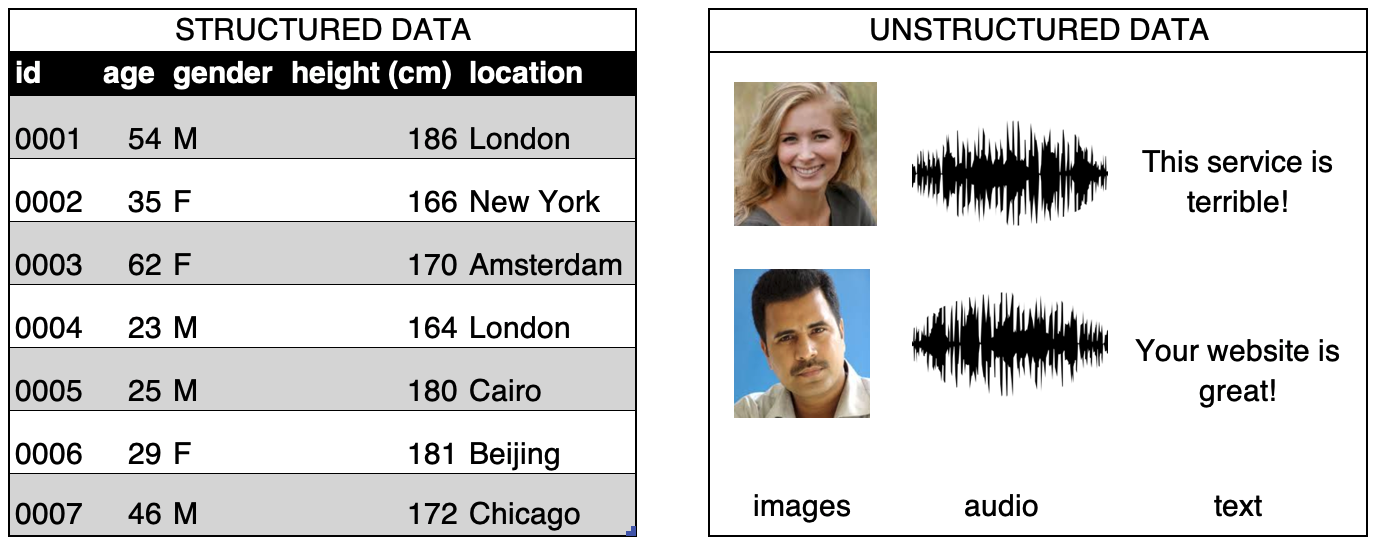
Figure 2-1. The difference between structured and unstructured data
图 2-1。结构化数据和非结构化数据的区别
When our data is unstructured, individual pixels, frequencies, or characters are almost entirely uninformative. For example, knowing that pixel 234 of an image is a muddy shade of brown doesn’t really help identify if the image is of a house or a dog, and knowing that character 24 of a sentence is an e doesn’t help predict if the text is about football or politics.
当我们的数据是非结构化的时,单个像素、频率或字符几乎完全没有信息。例如,知道图像的像素 234 是棕色的浑浊阴影并不能真正帮助识别图像是房子还是狗,并且知道句子的字符 24 是 e 并不能帮助预测是否文本是关于足球或政治的。
Pixels or characters are really just the dimples of the canvas into which higher-level informative features, such as an image of a chimney or the word striker, are embedded. If the chimney in the image were placed on the other side of the house, the image would still contain a chimney, but this information would now be carried by completely different pixels. If the word striker appeared slightly earlier or later in the text, the text would still be about football, but different character positions would provide this information. The granularity of the data combined with the high degree of spatial dependence destroys the concept of the pixel or character as an informative feature in its own right.
像素或字符实际上只是画布上的凹痕,其中嵌入了更高级别的信息特征,例如烟囱的图像或前锋一词。如果图像中的烟囱放置在房子的另一侧,图像仍将包含烟囱,但此信息现在将由完全不同的像素携带。如果“前锋”一词在文本中出现得稍早或稍晚,则文本仍将是关于足球的,但不同的角色位置将提供此信息。数据的粒度与高度的空间依赖性相结合,破坏了像素或字符本身作为信息特征的概念。
For this reason, if we train logistic regression, random forest, or XGBoost algorithms on raw pixel values, the trained model will often perform poorly for all but the simplest of classification tasks. These models rely on the input features to be informative and not spatially dependent. A deep learning model, on the other hand, can learn how to build high-level informative features by itself, directly from the unstructured data.
因此,如果我们在原始像素值上训练逻辑回归、随机森林或 XGBoost 算法,则训练后的模型通常对于除最简单的分类任务之外的所有任务都表现不佳。这些模型依赖于输入特征来提供信息并且不依赖于空间。另一方面,深度学习模型可以学习如何直接从非结构化数据中自行构建高级信息特征。
Deep learning can be applied to structured data, but its real power, especially with regard to generative modeling, comes from its ability to work with unstructured data. Most often, we want to generate unstructured data such as new images or original strings of text, which is why deep learning has had such a profound impact on the field of generative modeling.
深度学习可以应用于结构化数据,但其真正的力量,尤其是在生成建模方面,来自于其处理非结构化数据的能力。大多数情况下,我们希望生成非结构化数据,例如新图像或原始文本字符串,这就是深度学习对生成建模领域产生如此深远影响的原因。